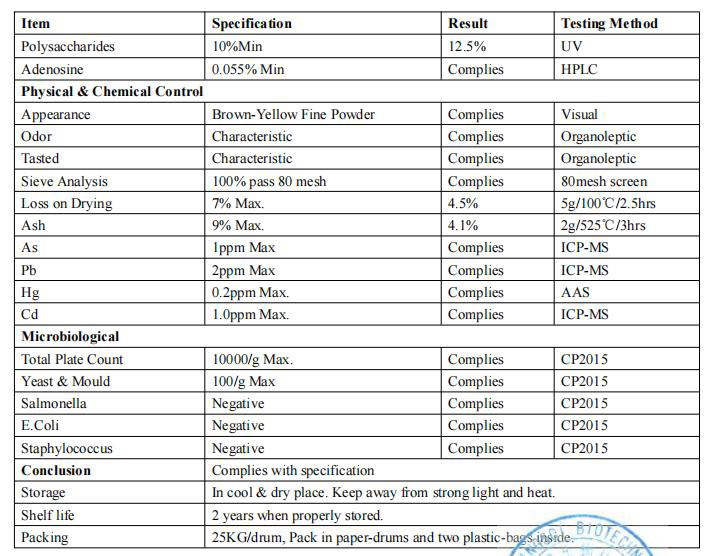
Appearance: Brown Powder
Test Method: UV
Sample: 10-20g for free
Active ingredients: Polysaccharide, Adenosine, Cordycepin
Certificates: ISO, HACCP, KOSHER, FDA
A combination of fungus and pupa makes up cordyceps militaris extract. It is a parasitic fungus that lives inside pupae. It can be intentionally produced on grains, but it typically grows in lepidopteran larvae. It may be produced industrially and is an edible fungus. The bioactive material concentration of Cordyceps militaris is very high, and it contains numerous useful bioactive components. The test confirmed that the content of Cordyceps is comparable to or even higher than that of wild Cordyceps since it mostly contains nucleosides, cordycepin, Cordyceps polysaccharides, superoxide dismutase (SOD), cordycepic acid, and other functional or therapeutic components.
1. Anti-cancer. The active ingredient of Cordyceps militaris, cordycepin, is an antibiotic that can interfere with human RNA and DNA synthesis, thereby inhibiting the growth of various tumor cells and promoting tumor cell apoptosis.
2. Immunomodulatory effects. Experimental studies have shown that Cordyceps militaris can regulate the humoral immunity and cellular immunity of mice, and can improve the phagocytic function of peritoneal macrophages.
3. Cordyceps militaris polysaccharide has antibacterial and anti-infective effects.
4. Antioxidant. Cordyceps can scavenge free radicals in the human body, significantly increase the energy value of cells, lower blood pressure, regulate blood viscosity, expand cardiovascular and cerebrovascular, and protect the heart muscle.
5. Lower blood sugar. Cordyceps militaris extract is also selected in clinical practice to treat diabetes.
6. Diuretic effect. It is mainly used in the clinical treatment of renal failure.
»» A group of fungi and insects called Ophiocordyceps sinensis: Only the larvae of the Cordyceps bat moth may host Ophiocordyceps sinensis as a parasite. The compound of pupa and fungus known as Cordyceps militaris: Artificially developed Cordyceps militaris parasitizes the larvae, pupae, and adults of insects. Silkworm pupae are frequently used as hosts by Cordyceps militaris.
»» Ophiocordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris both contain comparable sorts of nutrients, however their quantities vary. According to studies, Ophiocordyceps sinensis is less nutritious than Cordyceps militaris. Examples include the fact that the phosphorous (P) level of Cordyceps militaris is 3.5 times higher than that of Ophiocordyceps sinensis and the amino acid content of Cordyceps militaris is likewise higher.
»» The physical effects of Cordyceps militaris and Ophiocordyceps sinensis are comparable, and neither herb’s active ingredient is less potent than the other. The four primary active components found in both Cordyceps militaris and Ophiocordyceps sinensis include cordycepin, mannitol, Cordyceps polysaccharide, SOD enzyme, etc. When the contents of these four active components were compared, Cordyceps militaris was higher than Ophiocordyceps sinensis, with respective values of 4.17, 1.18, 1.08, and 3.19 times higher.